Austria’s largest mobility provider asked us to rebuild its internal control system (IKS) on SharePoint. The critical challenge was to represent recurring tasks, trigger them on schedule, and monitor their completion against strict criteria.
This article walks through the automation concept we implemented and the workflow that keeps every task auditable.
Requirements
- Automatically generate recurring tasks
- Assign the right people with clear accountability
- Provide structured testing and supervision workflows
- Close and archive every task in a compliant manner
Implementation
Everything starts with clearly defined task templates. Administrators describe every scenario with parameters that make each recurring task measurable and traceable.
Key parameters per task definition
- Name: Title of the task to be created
- Duration: Number of days assigned testers have to close the task
- Interval: Recurrence frequency (for example monthly or quarterly)
- Tester: Person responsible for the execution
- Supervisor: Person who validates the outcome
Because the customer still uses an on-premises environment, we built a SharePoint Timer Job. It evaluates all definitions every day and spins up new tasks when they fall due. A companion workflow notifies testers via email as soon as work is assigned so nothing slips through the net.
Each department maintains its own list, ensuring that only authorized staff members can create or edit tasks within their area.
Reviewing recurring tasks
Testers document their findings directly in the assigned task:

Closing recurring tasks
Supervisors check the submitted evidence, reassign the task when rework is needed, or approve the result.
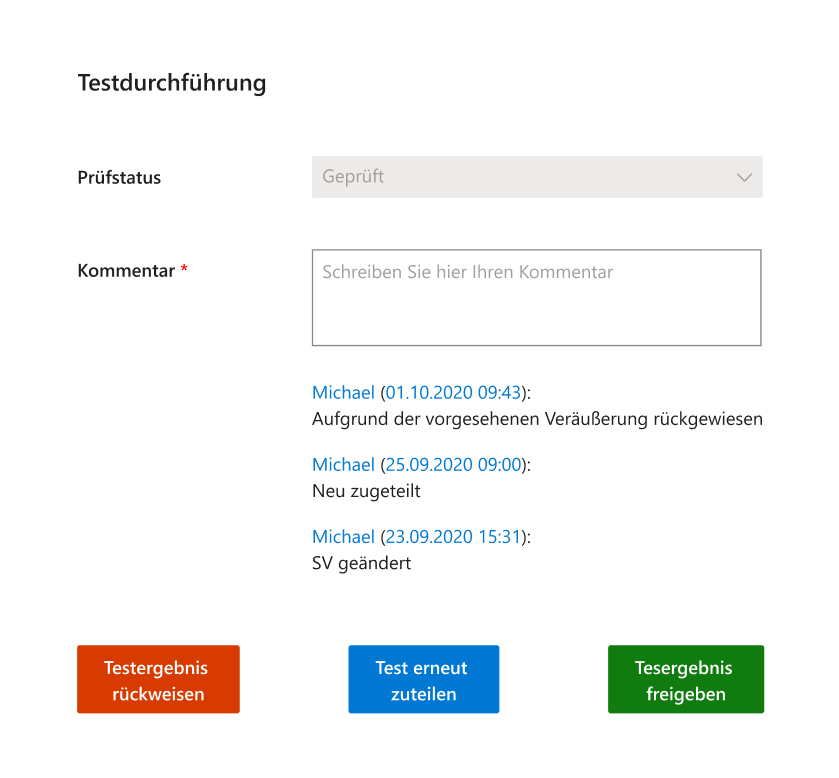
This loop continues until the task is approved or the allotted time expires. If the deadline passes, the workflow closes the task automatically and archives it with the status “unchecked”.
Architecture insights
The overall solution is organized by department. Each unit has its own pool of employees, and tasks can only be assigned inside that pool. Layered permissions guarantee that people only see the tasks belonging to their department.
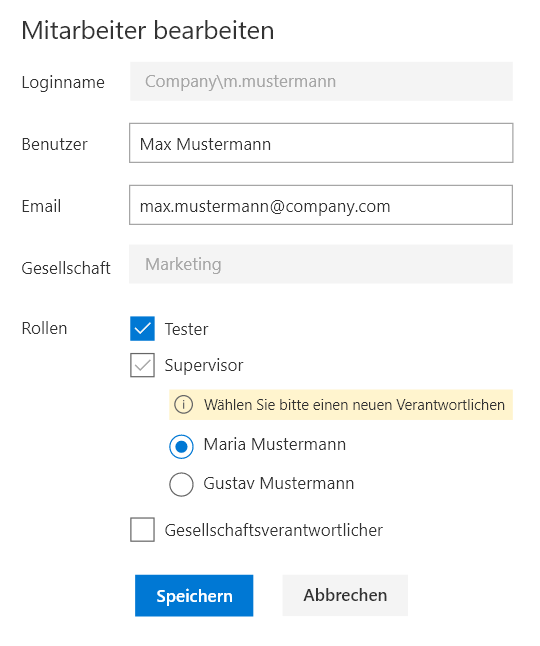
Roles and master data maintenance
All users and their roles are stored in a central employee list. If a role changes, the system propagates the new permissions to every active task automatically.
Versioned communication
Every exchange between testers and supervisors is stored as a versioned comment trail inside the task, so the audit path remains intact at all times.
Wrap-up
Need a similar setup? Reach out to us. You can also explore how we automate recurring tasks with Microsoft Power Automate and Planner.
